动载荷下固体推进剂损伤演化原位成像研究

打开文本图片集
YUAN Yongxiang],LIU Yuexun1, ZHAO Meng², WANG Long, HOU Chuantao³, WANG Xuanjun²,WU Shengchuan1 (1.StateKeybratoryofilitViclestem,outhestJongUversityengduoichind; 2.ZhijianLaboratory,RocketForce UniversityofEngineering,Xi'an7oo25,Shaanxi, China; 3. Key Laboratory ofScience and Technology on Reliability and Environmental Engineering, Beijing Institute of Structure and Environment Engineering, Beijing 1Ooo76, China)
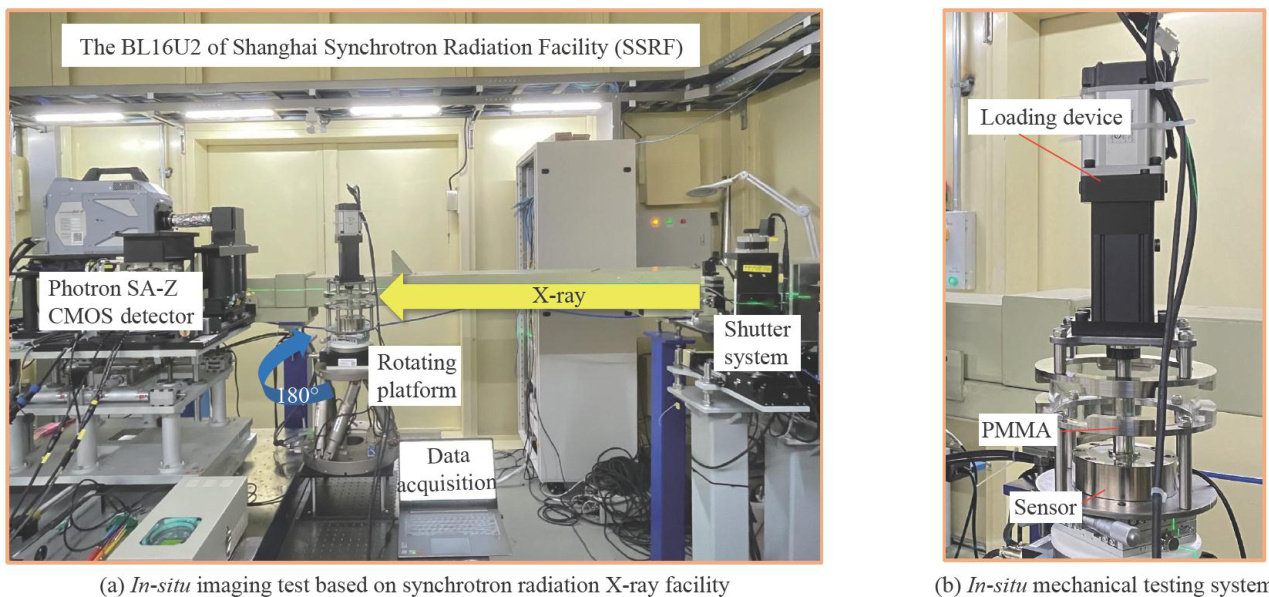
Abstract: Structural damages insolid propelants can lead to combustion anomalies and affect ballstic performance. Utilizing synchrotronradiation X-raycomputed tomography technologyandanin-situ mechanicalloading testsystem,themacro-meso structures ofnitrate esterplasticized polyether (NEPE)solid propelant wereobserved in-situ atcompressiveratesof 0.1,1.0, and 5.0mm/s .The compressive process employed an intermitent loading mode.With loading paused each time the preset displacement was reached to enablescaning imaging,therebycapturingthestateof the propelantat specific phases during compression.Follwing the in-situ imaging experiment,the tomographic images of the samples were processed through projection correction and phase recovery using PITRE and PITRE_BM software,followed by image bit-depth conversion to obtain8-bit2Dgrayscale slices.Through 3Dreconstruction,thetypical damagesand evolutionary behaviorsofthe solid propellant wereanalyzed,exploring the macroscopic deformationas wellasthe distribution and propagation pattemsof interalmicro-cracks.Resultsindicatethat most micro-cracksnucleateand growatthe interface between filedparticlesand the matrix, with meso-pore evolution being rate-dependent. Unlike the continuous damage growthunder tensile loading,the nucleation,growth,andclosureof poresoccursimultaneouslyduringcompresion.Under high-rateuiaxialcopressive loading,thesolidpropelantexibitscharacteristictrumpet-shapeddeformation,withspatiallydistributedcrackspriarily located around the propellant.Macroscopic surface damage results from micro-crack propagation betwee near-surface particlesandthematrix,withrackpropagationrelatedtothespatiallocationoffiledparticles.Transversalandaxialcrack propagation modes existunderdynamiccompressveloading,withthe transitionfromverticall tohorizontallyorientedcracks in the matrix leading to crack closure.
Keywords:solid propellant;in-situ dynamiccompression;damage rate-related behavior; internal damage evolution; synchrotron radiation 3D tomography
固体推进剂是一种典型的非均相颗粒增强复合材料,广泛用于先进航空航天装备动力系统[1-4]。(剩余14490字)