良性前列腺增生术后高凝状态的危险因素分析

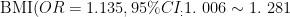
打开文本图片集
Analysis of the risk factors of hypercoagulable state after surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia
WAN Quan1,² ,SHAO Cong ,LIU Zhe1 ,WEN Yongan² ,YANG Lin1 (1. Department of Urology,The First Afiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University,Xi'an 710001; 2.Department of Urology,Afiliated Hospital of Xizang Minzu University,Xianyang 712000; 3.Hebi Institute of Engineering and Technology,Henan Polytechnic University,Hebi 4580oo,China)
ABSTRACT:ObjectiveTo analyze the factors influencing hypercoagulable state in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) after surgery,soas to provide reference for preventing postoperative thrombosis in BPH.MethodsA retrospective analysis was conductedon the clinical dataof 3O7 BPH patients whounderwent surgery in the Departmentof Urology atthe First Afiliated Hospitalof Xi'anJiaotong Universityduring Apr.2022 andSep.023.Patients were divided into the hypercoagulablestate groupand non-hypercoagulable state groupbasedon the presence of abnormal postoperative coagulation parameters.Single factorand binarylogisticregresion analysiswereused toscreenrisk factorsaffecting postoperative blood hypercoagulability in BPH patients. ResultsAmong the 3O7 BPH patients,45 ( 14.66% )developed a hypercoagulablestatepostoperatively.Univariateanalysisrevealedstatisticallysignificantdiferences between the hypercoagulableandnon-hypercoagulablegroupsregarding patientsage,lengthof hospitalstay,bodyma index(BM)stor of hypertension,history of diabetes,and blood type ( P<0.05 ).Binary logistic regression analysis identified BMI ( OR=1.135 , (20 95%CI:1.006-1.281,P=0.039) ,history of hypertension ( OR=2.342,95%CI:1.103-4.927,P=0.027) ,and blood type ( OR=2 .2 70,95%CI:1. 066-4. 836 , P=0. 034 ) as independent risk factors for postoperative hypercoagulable state. ConclusionNon-Oblood type,highBMI,and historyof hypertensionare independent risk factors for theocurrence of hypercoagulable state following surgery for BPH.
KEY WORDS: benign prostatic hyperplasia; hypercoagulable state; lower urinary tract symptoms
中图分类号:R697 文献标志码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-8291.2025.08.008
良性前列腺增生(benignprostatichyperplasia,BPH)是引起中老年男性排尿障碍最常见的疾病之[1],其发病率随着年龄的增长而升高。(剩余8373字)