PBST/PHA/木质素三元复合材料薄膜的制备及性能

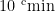
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TB33 文献标志码:A
Preparation and Properties of PBST/PHA/Lignin Ternary Composite Films
LIN Jinhui, SI Jundong, ZHANG Yan (SchoolofMaterialsScienceandEngineering,EastChina UniversityofScienceandTechnology,Shanghai237,China)
Abstract:Poly (butylene sucinate-co-terephthalate) (PBST)/ polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)/lignin composite films were prepared by casting method.Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR),diferential scaning calorimetry (DSC)and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)were used to characterize the structure,thermal properties,mechanical properties and crystallzation propertiesof thecomposites.Results showed that no newchemical bond was formed in the melt blending proces.The thermal stabilityof thecomposite materials was improved.With the increaseoflignincontent,the mechanical properties ofthe composites first increased and then decreased. Under the condition of lignin mass fraction of 20% ,the tensile strength and elongation at break reached 9.2MPa and 848.0% , respectively. Moreover, the melt index and water vapor transmittnce of the composite film reached 15.6g/10min and 31.6g/(m2⋅d) ,respectively, demonstrating excellent melt processing performance and water barier performance. The composite films also had excelent UV blocking properties (UV absorption rate is greater than 99% ),and could delay UV aging of the films.The results of soil degradation experiment showed that thedegradationrateof thecomposite filmcould reachabout 10% in 120d ,andthemechanicalpropertiesof the composite film decreased significantly.Theseresults indicatethattheintroductionof lignin wasrapidlydegraded by microorganisms insoil,whichcouldeffectivelyacelerate thesoil degradationof thin films.Inconclusion,thismethod providesanapproach to improve the properties of polymers through melt blendingand expands the applicationsof lignin in multi-component polymer materials.
Key words: poly (butylene sucinate-co-terephthalate); polyhydroxyalkanoates;lignin; film;melt blending
传统塑料力学性能优良且成本低廉,但降解缓慢,并在降解过程中产生大量微塑料,对环境造成严重威胁,因此可降解塑料已成为研究热点[1]。(剩余12585字)