枇杷幼嫩果肉及种子原生质体制备体系优化

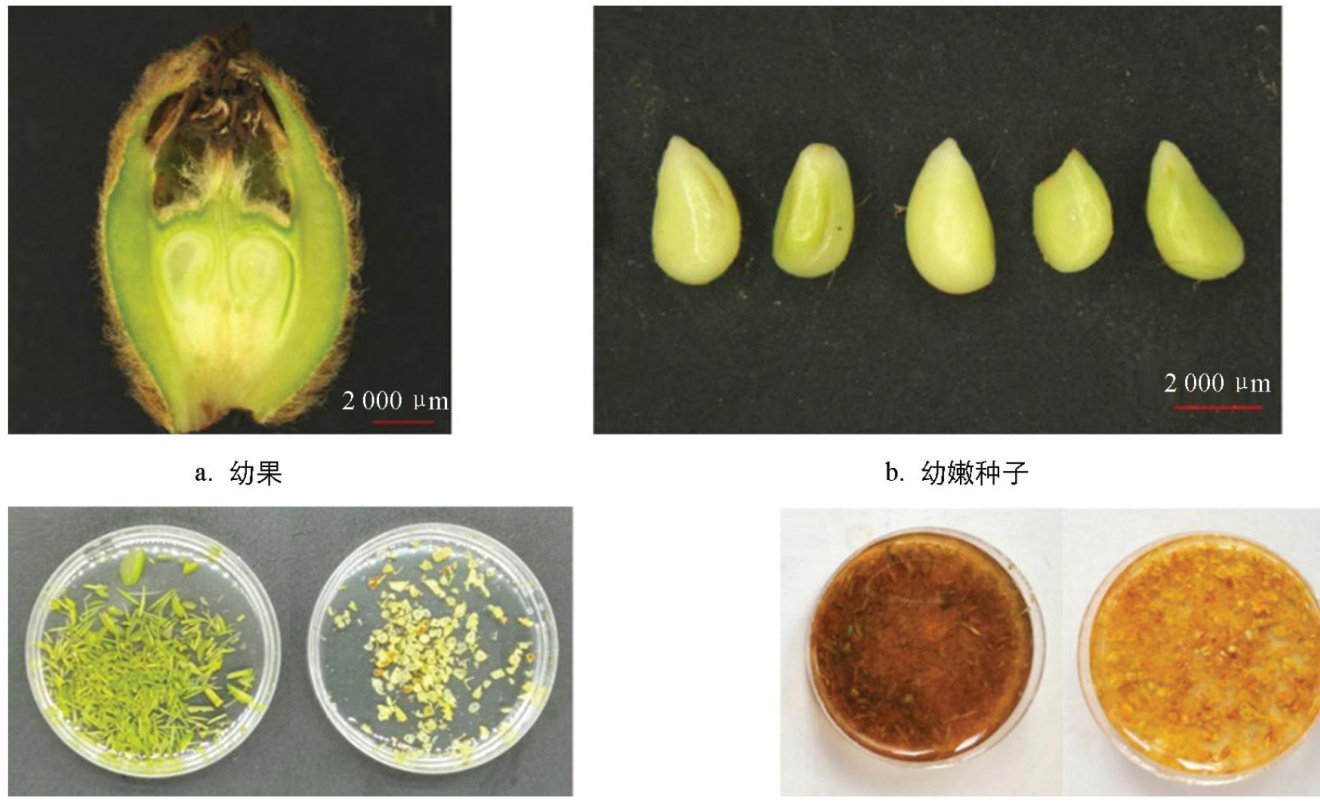
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S661.9 文献标识码:A
Optimization of Protoplast Isolation System from Young Fruit Pulp and Seeds of Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica)
WANG Shuming1, HUANG Hanwen1, WANG Liyun1,ZHANG Yin1, XIA Yan1, JING Danlong1, GUO Qigao 1 ,LIANG Guolu1, LIN Shoukai², HE Qiao1
1.Key Laboratory of Agricultural Biosafetyand Green Production of Upper Yangtze River(Ministry of Education)/ College of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture, Southwest University, Chongqing 4O0715,China; 2.Key Laboratoryof Loquat Germplasm Innovationand Utilization(Putian University),Putian Fujian35110o,China
Abstract:To optimize the method for protoplast isolation from loquat,pulp and seeds from young fruits of loquat cultivar‘Xingning No.1’ were employed as materials for study of protoplast isolation with enzymatic digestion. Key parameters,including enzyme types and concentrations,digestion time,and shaking speed,were systematically optimized by evaluating protoplast yield and viability. The eficient protocol for isolation of protoplast from loquat young fruit pulp was the digestion with combination of 4.6%(w/v) ( cellulase RS and 2.6%(w/v) ) macerozyme R-l0 enzyme for 11h with shaking speed of 50r/min under dark. The yield and viability of protoplasts was 1.66×106g-1 protoplasts and 62.29% ,respectively. For isolation of protoplasts from young seeds, maximum efficiency was achieved by digestion with 4.4% (204 Cellulase RS and 2.6% Macerozyme R-10 for 10h under dark with 50r/min of shaking,which produced (204 7.583×105g-1 protoplasts with 90.83% of viability. This efficient protocol for isolation protoplasts from young fruit pulp and seeds could overcome the seasonal limitations of traditional mesophyll protoplast systems in loquat, enabling year-round protoplast preparation for genetic researches and breeding.
Key words: loquat; protoplast; isolation;enzymatic digestion; immature fruit pulp;immature seeds
枇杷(Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.)属于蔷薇科枇杷属,是我国重要的亚热带常绿果树[1],因其果实口感细腻多汁以及丰富的药用价值而深受人们喜爱,目前已在世界范围内广泛栽培。(剩余14356字)