中山市40岁及以上居民高血压影响因素的差异性分析

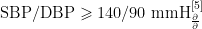
打开文本图片集
【中图分类号】R544.1 【文献标识码】A
Difference analysis of hypertension risk factors of residents aged 40 and above in Zhongshan
CHENJie1,LIN Hai1,LI Chuan²
1.Department of Noncommunicable Diseases Control and Prevention, Zhongshan Center for DiseaseControl and Prevention, Zhongshan 5284oo, Guangdong Province, China
2.Institute for Prevention and Control of Chronic Noncommunicable Diseases,Guangdong ProvincialCenterforDisease Controland Prevention,Guangzhou 511430,ChinaCorresponding author: LI Chuan,Email: 13076879515@163.com
【Abstract】Objective To analyze the risk factors for hypertension and the differences across gender and age groups among residents aged 40 years and older in Zhongshan City, to provide evidence for regional hypertension prevention and control policies. Methods Data were obtained from the National Stroke High-Risk Population Screening and Intervention Project. A multistage cluster random sampling method was used to select residents who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria as study participants. Information on sociodemographic characteristics,lifestyle,and family history was colected through questionnaires.Physical and biochemical examinations were conducted to obtain body massindex,blood pressure,heart rate,fasting blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin,and homocysteine levels.Logistic regresson analysis was used to assess the risk factors for hypertension and diferences across gender and age groups. Results A total of 7,015 participants were included,3,582 people suffered from hypertension, with a hypertension prevalence rate of 51.1% .Multivariate Logistic regression analysis identified age,gender,regular alcohol consumption,family history of hypertension,history of stroke or transient ischemic attack, use of lipid-lowering medications, waist circumference, heart rate,fasting blood glucose,low-density lipoprotein cholesterol,and homocysteine levels as independent predictors of hypertension ( (P<0.05) . The risk factors for hypertension prevalence differed significantly between gender groups and age groups. Conclusion Multiple risk factors contribute to hypertension among residents aged 40 years and older in Zhongshan City, with notable diferences across gender and age groups.
【Keywords】Hypertension; Risk factors; Age; Gender
高血压是全球范围内最常见的慢性病之一[],我国有三分之一的心血管死亡归因于高血压,严重影响国民健康和社会经济发展[3-4],早期筛查和预防高血压的发生发展成为亟待解决的公共卫生问题。(剩余12999字)