保湿时间对小麦赤霉病抗性鉴定结果的影响

打开文本图片集
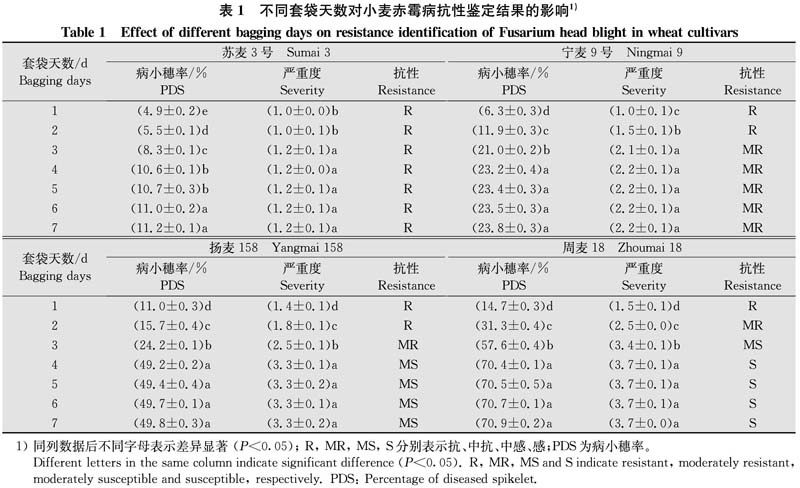
摘要 为优化黄淮麦区小麦赤霉病抗性鉴定方法,于2020年在河南农业大学许昌校区试验田对4个小麦品种进行单花滴注赤霉病抗性鉴定,分析不同套袋保湿天数对病情严重度的影响,并利用与主效抗病基因Fhb1连锁的功能标记TaHRC-STS对其进行分子检测。结果显示:抗病品种‘苏麦3号’‘宁麦9号’携带该基因,而感病品种不携带;套袋1~7 d处理均引起赤霉病菌侵染,病情严重度随着套袋时间的延长而显著增加,在套袋4~7 d处理下,同一抗、感品种的严重度间无显著差异;且感病品种4~7 d的严重度显著高于1~3 d处理(P
关键词 小麦; 赤霉病; 保湿时间; 禾谷镰刀菌; 抗性鉴定
中图分类号: S435.121.45
文献标识码: A
DOI: 10.16688/j.zwbh.2020704
Abstract In order to optimize the identification method of Fusarium head blight (FHB) resistance in Yellow and Huai River Valley wheat region of China, the FHB resistance of four wheat cultivars planted in experimental field of Xuchang campus of Henan Agricultural University were identified by single floret injection in 2020. The effects of different moisturizing days on the disease severity were analyzed, and then molecular analysis of the four wheat cultivars was performed using TaHRC-STS, a functional marker linked to Fhb1 gene of FHB resistance. The results indicated that resistant cultivars ‘Sumai 3’ and ‘Ningmai 9’ carried Fhb1 gene, while susceptible cultivars did not carry it, and the disease severity increased significantly with the extension of bagging time, and there was no significant difference between the same resistant and susceptible cultivars under bagging for four days to seven days. The severity of susceptible cultivars in 4-7 days was significantly higher than that in 1-3 days, and the evaluation of resistance was also different from that in 1-3 days, which indicated that Fhb1 gene could enhance the FHB resistance. In the identification of FHB resistance, bagging and moisturizing for four days was better in Yellow and Huai River Valley wheat region of China.
Key words wheat; Fusarium head blight; moisturizing time; Fusarium graminearum; resistance identification
小麦赤霉病主要是由禾谷镰刀菌Fusarium graminearum Schw.引起的小麦真菌病害。(剩余9081字)