TCT检测筛查ASCUS发生HSIL的高危因素分析

打开文本图片集
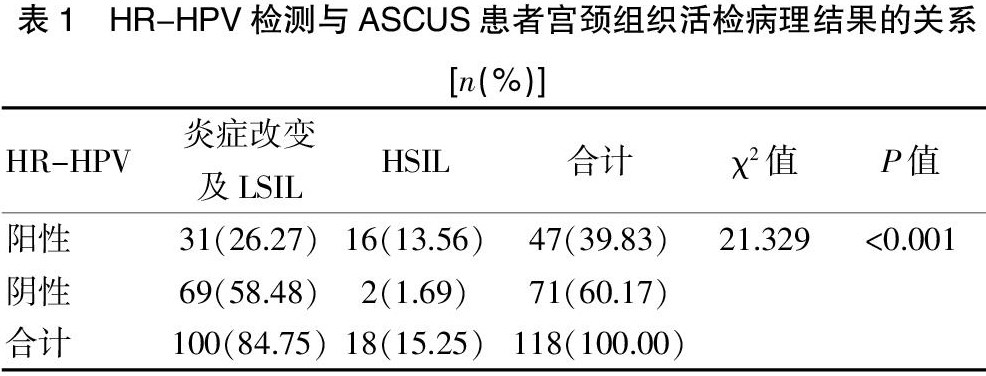
[摘要] 目的 研究分析TCT检测筛查不能明确意义的非典型鳞状细胞(ASCUS)发生HSIL的高危因素。方法 回顾性分析2017年1月至2021年4月于广东省汕头市第三人民医院妇产科经TCT检测筛查提示为ASCUS患者118例的临床资料,分析ASCUS发生HSIL的高危因素。 结果 118例TCT诊断为ASCUS患者经活检病理金标准,其中炎症改变27.97%(33/118)、LSIL56.78%(67/118)、HSIL15.25%(18/118),HR-HPV检测HSIL的敏感度为88.89%(16/18),阴性预测值为97.18%(69/71);研究组与对照组在首次性生活年龄、流产次数、HR-HPV及绝经比较,差异有统计学意义(P
[关键词] TCT;ASCUS;HSIL;高危因素
[中图分类号] R711.74 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2022)12-0057-03
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the high risk factors of HSIL in atypical squamous cells (ASCUS) which cannot be clearly screened by TCT. Methods The clinical data of 118 ASCUS patients screened by TCT in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology in the Third People′s Hospital of Shantou City in Guangdong Province from January 2017 to April 2021 were analyzed retrospectively. The high risk factors of HSIL in ASCUS were analyzed. Results Among 118 patients diagnosed as ASCUS by TCT, taking biopsy pathology as the gold standard, patients with inflammatory changes accounted for 27.97% (33/118), LSIL for 56.78% (67/118) and HSIL for 15.25% (18/118). Patients who were detected by HR-HPV for the sensitivity of HSIL accounted for 88.89% (16/18), and the negative predictive value was 97.18% (69/71). There were significant differences in age of first sexual life, abortion times, HR-HPV and menopause between study group and control group (P
[Key words] TCT; ASCUS; HSIL; High risk factors
宫颈癌是女性恶性肿瘤发病率居第2位的肿瘤,据国际癌症研究机构2020年流调报道,我国新发病例约11万,死亡病例约6万,严重危害女性生命安全,因此,早筛早诊早治控制宫颈癌发病率及死亡率至关重要[1]。(剩余5480字)