下肢动脉硬化闭塞症置管溶栓联合腔内治疗的应用研究

打开文本图片集
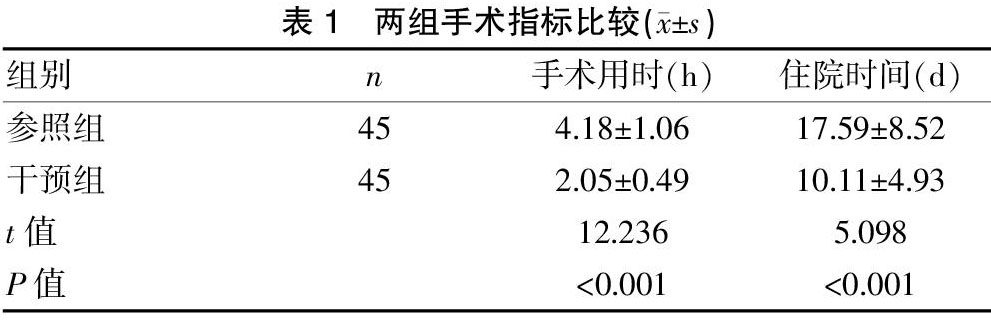
[摘要] 目的 对比置管溶栓结合腔内介入治疗下肢动脉硬化闭塞症(ASO)的临床价值。方法 纳入2015年9月至2020年9月山东省潍坊市益都中心医院收治的ASO患者90例,随机分为干预组、参照组,各组均45例,前者提供置管溶栓+腔内介入治疗,后者仅行腔内介入治疗,对比两组疗效及临床指标。结果 干预组血管开通及截肢率均优于参照组,差异有统计学意义(P
[关键词] 介入治疗;下肢动脉硬化闭塞症;置管溶栓;临床疗效
[中图分类号] R543.5 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2022)10-0107-04
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the clinical value of catheter-directed thrombolysis combined with endovascular intervention for lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans (ASO). Methods A total of 90 patients with ASO admitted to Weifang Yidu Central Hospital of Shandong Province from September 2015 to September 2020 were included in this study. They were divided into the intervention group and the control group according to the randomized grouping principle, with 45 patients in each group. The intervention group was treated with catheter-directed thrombolysis + endovascular intervention, while the control group was treated with endovascular intervention. The efficacy and clinical indexes were compared between the two groups. Results The vascular patency rate was higher and the amputation rate was lower in the intervention group than those in the control group, with statistically significant differences (P
[Key words] Intervention; Lower extremity atherosclerosis obliterans; Catheter-directed thrombolysis; Clinical efficacy
下肢动脉硬化闭塞症(lower extremity atherosclerosis obliterans,ASO)主要是指动脉粥样硬化造成动脉闭塞或狭窄诱发的下肢缺血疾病,患者主要表现为下肢缺血性疼痛[1]、肢体坏疽与间跛等,常合并全身多处动脉硬化病变,影响病人的身体健康及寿命。(剩余7702字)