磁共振波谱成像对颅内异常强化病灶的诊断分析

打开文本图片集
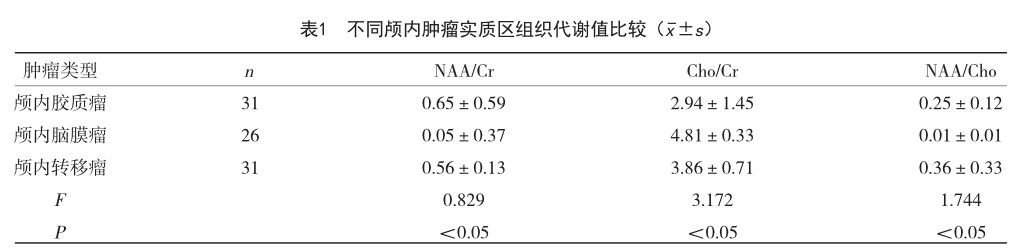
【摘 要】目的 探究磁共振波谱成像对颅内异常强化病灶的诊断意义。方法 选取2021年12月-2022年6月某三甲医院收治的88例颅内肿瘤患者为研究对象,对所有患者实施磁共振波谱成像诊断,比较不同颅内肿瘤实质区、邻近水肿区的磁共振波谱成像表现(Cho/Cr、NAA/Cho、NAA/Cr)。结果 88例颅内肿瘤患者的病理诊断结果中确诊为颅内胶质瘤有31例(35.22%),颅内脑膜瘤有26例(29.54%),颅内转移瘤有31例(35.22%);三种不同的颅内肿瘤检测实质区NAA/Cr、Cho/Cr、NAA/Cho水平比较,差异有统计学意义(P
【关键词】磁共振波谱成像;颅内异常强化病灶;诊断
中图分类号:R445.2 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1004-4949(2022)24-0083-04
Diagnostic Analysis of Intracranial Abnormal Enhancement Lesions by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
DONG Yi-ming
(School of Biomedical Engineering and Medical Imaging, Hubei Institute of Science and Technology, Xianning 437100, Hubei, China)
【Abstract】Objective To investigate the diagnostic significance of magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging for abnormal intracranial enhancement lesions. Methods A total of 88 patients with intracranial tumors admitted to a tertiary hospital from December 2021 to June 2022 were selected as the research objects. All patients were diagnosed by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging findings (Cho/Cr, NAA/Cho, NAA/Cr) of different intracranial tumor parenchyma and adjacent edema areas were compared. Results Among the 88 patients with intracranial tumors, 31 patients (35.22%) were diagnosed as intracranial gliomas, 26 patients (29.54%) were intracranial meningiomas, and 31 patients (35.22%) were intracranial metastases. There were significant differences in the levels of NAA/Cr, Cho/Cr and NAA/Cho in the three different intracranial tumors (P
【Key words】Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging; Abnormal intracranial enhancement lesions; Diagnosis
患者脑部或者脊髓等部位的中枢神经系统出现的疾病统称为中枢神经系统疾病[1]。(剩余3837字)