下台阶建筑屋顶烟肉排放污染物扩散特性研究

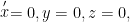
打开文本图片集
中图分类号: X511 文献标志码:A
Abstract: Based on a numerical model validated by wind tunnel experiments, the influence of atmospheric stability, characterized by the bulk Richardson number (Rib) in the range of -0.21 to 0.79, on the diffusion of pollutants from roof chimneys on step-down buildings was investigated. The results indicate that the flow field and pollutant distribution within the street canyon are significantly altered by atmospheric stability.Under stable conditions (Rib>0) ), vertical convection within the street canyon was weak. At Rib=0.43 , the dimensionless velocity difference (O.25) on the vertical center plane (y/H=0) was reduced by 13.80% compared to that under neutral conditions. At Rib=0.79 , the maximum dimensionless concentration (4.76) at the pedestrian breathing level was increased by 18.70% . Under unstable conditions (Rib<0) ,vertical convection was enhanced, with increased wind speed near the ground, leading to a notable decrease in pollutant concentration. At Rib=-0.19 , the dimensionless velocity difference (O.32) on the vertical center plane was increased by 10.34% .At Rib=-0.21 ,the maximum dimensionless concentration (O.88) at the pedestrian breathing level was decreased by 78.19% . The paterns of local urban flow fields and pollutant dispersion under different atmospheric stability conditions are revealed, providing a theoretical basis for targeted air quality improvement.
Keywords: step-down building; wind tunnel experiment; numerical simulation; atmospheric stability; pollutant diffusion
城市建筑物(工业建筑、医院、住宅楼等)屋顶烟囱释放的废气污染物,可能在不利扩散条件下影响相邻建筑室内和街道近地面空气质量。(剩余13023字)