厨余垃圾厌氧消化沼渣与物流垃圾混合燃烧过程气体污染物排放特性研究

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TK6;X78 文献标志码:A
Abstract: Incineration is a promising way for the volume reduction of municipal organic waste. Food waste-derived anaerobic digestate (AD) contains high moisture, abundant ash, and low calorific value, unstable combustion and severe slagging and fouling always occur during combustion. Co-combustion of AD with high-calorific value and low-ash cardboard (CB) and polyethylene (PE) from waste logistics packaging can improve its combustion performance effectively. However, the gaseous pollutants emission characteristics such as HCl, NOx, and SO2 are crucial for their clean incineration. The influence of combustion temperature, CB blending ratio, and PE blending ratio on the gaseous pollutants emissions during the combustion process was examined. Results indicate that higher combustion temperature enhances the emissions of HCl and SO2 while it reduces NO emission. The co-combustion process of AD, CB, and PE releases more HCl due to the interaction. Adding PE favors the formation of gaseous pollutants such as NO and SO2 . It is critical to control PE blending ratio in the practical project. This work can provide a theoretical reference for the clean co-incineration of AD and waste logistics packaging.
Keywords: polyethylene;cardboard;interaction;HCl; NO; SO2
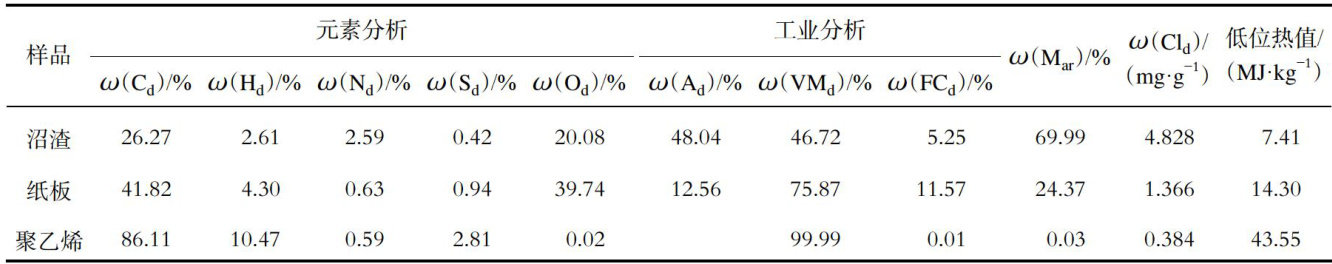
我国从2019年开始推行垃圾强制分类后,厨余垃圾分出量急剧增加。(剩余14209字)