某超高层建筑玻璃幕墙塔冠空调气流组织及热舒适性研究

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TU831 文献标志码:A
Abstract: Significant temperature stratification occurs in the interior of tall, large-volume buildings, compounded by the impact of solar radiation on transparent enclosure structures. Currently, there are no established standards or methods specifically guiding the design of airconditioning airflow organization for such large spaces, necessitating customized designs to better meet indoor thermal comfort requirements and achieve energy-efficient,low-carbon operation of heating,ventilation and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations were employed to evaluate cooling air-conditioning schemes for a 55-meter-high transparent tower crown in a super-tall building during summer, considering the combined effects of air temperature and solar radiation on thermal comfort. Analysis of four different airconditioning scheme combinations led to an optimized airflow organization strategy. The results show that a combination of side supply and top-and-bottom supply airflow achieves the lowest fan energy consumption while maintaining occupant comfort, thus realizing energy savings. This research provides a valuable reference for summer air-conditioning design in large-volume buildings with extensive transparent enclosures and represents a beneficial application of CFD simulations in assisting HVAC system design.
Keywords: large space building; transparent enclosure; CFD simulation; thermal comfort;solar radiation
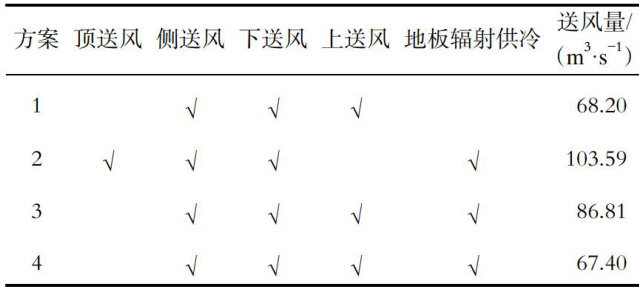
玻璃幕墙等透明围护结构是现代商业建筑普遍采用的立面形式。(剩余10296字)