硒镁纳米颗粒的制备及其抗菌效果评价

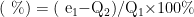
打开文本图片集
[中图分类号] R318.08;R587.2 [文献标志码]A [文章编号] 1671-7783(2025)04-0355-06
DOI: 10.13312/j.issn.1671-7783.y240041
[引用格式].硒镁纳米颗粒的制备及其抗菌效果评价[J].江苏大学学报(医学版),2025,35(4): 355-360.
Preparation of selenium-magnesium nanoparticles and their antibacterial effect evaluation
MENG Ye, ZHANG Chun,SHEN Haijun (School of Medicine,Jiangsu University,ZhenjiangJiangsu 212O13,China)
[Abstract]Objective:To integrate the two elements of selenium and magnesium into nanoparticles to prepare selenium-magnesium nanoparticles,and explore their antibacterial effect and antibacterial mechanism. Methods: The morphology and particle size distribution of selenium-magnesium nanoparticles were characterized by transmisson electron microscopy and nano-particle size analyzer. The antibacterial effect of selenium-magnesium nanoparticles was evaluated by plate counting method,disk diffsion method,and bacterial live/dead staining method. The content of reactive oxygen species in bacteria after exposure to nanoparticles was detected by DCFH-DA fluorescence probe to explore its potential antibacterial mechanism.Results: Selenium-magnesium nanoparticles are irregular spherical under transmission electron microscopy,and the particle size is mainly concentrated in the range of 5O-70 nm. They exhibit excellent antibacterial properties,especially against Staphylococcus aureus and methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus.The potential antibacterial mechanism involves induction of reactive oxygen species production in bacteria. Conclusion: The prepared selenium-magnesium nanoparticles exhibitgood antibacterial properties,ithas been preliminarilydemonstrated that bacterial kiling is achieved by inducing the production of reactive oxygen species within bacterial.
[Key words]selenium; magnesium; nanoparticles;antibacterial; reactive oxygen species; diabetic ulcer
糖尿病的发病率正在逐年攀升,2021年全球糖尿病患者约为5.37亿,预计到2045年将高达7.83亿[1]。(剩余8301字)