耕地“非粮化”空间特征识别与影响因素分析
——以济南市长清区为例

打开文本图片集
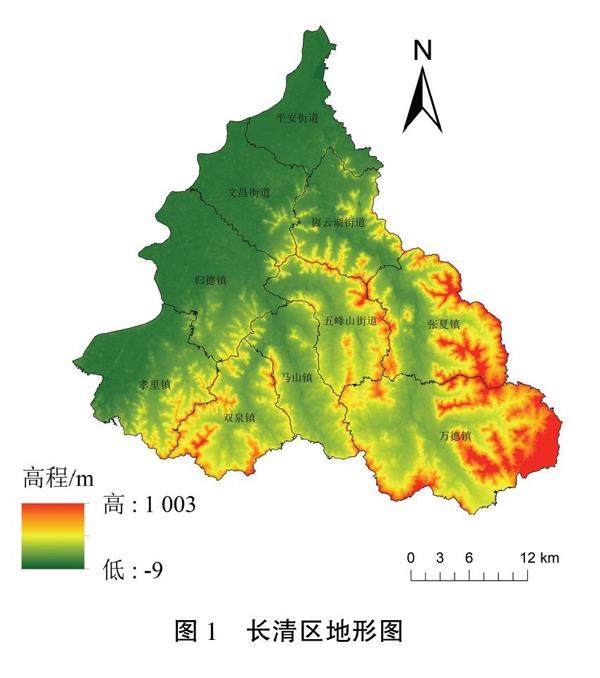
摘要:合理测算区域非粮化水平、识别耕地非粮化空间分布特征及其影响因素,可为保护粮食安全、促进耕地精细化管理提供科学的参考依据.以济南市长清区为研究对象,分析研究区耕地非粮化现状及类型,综合运用空间自相关分析、热点分析、地理加权回归模型等研究方法,以识别长清区非粮化水平空间分布特征、影响因素及其作用效应的空间差异性.研究结果表明:长清区耕地非粮化总面积共计26503.83ha,非粮化水平为46.28%;非粮化水平的空间相关性较为显著,存在明显的集聚现象;高程、有机质含量、距河流距离与非粮化水平呈正相关:而耕地连片度、距城镇距离、距居民点距离与人均GDP与非粮化水平呈负相关
关键词:耕地;非粮化;空间特征;地理加权回归模型
中图分类号:F323.2文献标志码:A
Spatial Characteristics Identification and Influencing Factors Analysis of "non-grain" Cultivated Land --A Case of Changging District of Jinan City
DONG Dekun, WU Yifan
(School of Management Engineering, Qingdao University of Technology, Qingdao 266520, China)
Abstract: Reasonably estimating the level of degrainization in a region, identifying the spatial distribution characteristics of degrainization of cultivated land, and analyzing its influencing factors can provide scientific reference for protecting food security and promoting fine management of cultivated land. Taking Changqing District of Jinan City as the research object, this paper analyzes the current status and types of degrainization of cultivated land in the study area. Various research methods are comprehensively used, including spatial autocorrelation analysis, hot spot analysis, geographical weighted regression model etc., to identify the spatial distribution characteristics, influencing factors and spatial differences of the effects of degrainization in Changqing District. The research results show that the total area of non-grainarable land in Changqing is 26 503.83 ha, and the degrainization level was 46.28%. The spatial correlation of degrainization level is significant, and there is an obvious agglomeration phenomenon. The elevation, organic mater content and distance from river are positively correlated with the level of degrainization while the contiguity of cultivated land, distance from urban area and distance from residential area are negatively correlated with per capita GDP and degrainization level.
Key words: cultivated land; degrainization; spatial characteristics; geographical weighted regression model
中国作为世界上人口最多的国家,保障粮食生产、保护粮食安全是关系到国家社会经济稳定发展的重大战略问题2,中国政府也保持着高度关注.在过去的十几年里,我国通过建立较为完整的耕地保护政策体系,以有效减少因城市扩张而导致的耕地大规模流失.但仅是关注耕地面积的流失和耕地向建设用地的转化还较为片面,受粮食作物产出效益低、耕地土壤退化等因素的影响,耕地内部的非粮化现象日益突出,并成为威胁粮食安全和社会稳定的潜在因素[3]
近年来,土地资源利用领域相关学者们围绕耕地非粮化进行了大量研究.在耕地非粮化空间分异与影响因素方面,陈浮等研究发现中国非粮化面积主要集中于北部与中南部,高非粮化率主要集中于新疆、贵州和东南沿海地区,且呈现出不同的空间聚集特征.何鑫等采用空间自相关、热点分析等方法深度剖析了耕地非粮化的空间分布规律.LiY等6基于空间自相关分析与地理加权回归对江苏省溧阳市非粮食耕地数量特征和空间分布进行了研究,并对其聚类特征和机制进行了探讨。(剩余5809字)