基于眼动追踪技术的冀南乡村风貌视觉感知优化研究

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TU982.29 文献标识码:A
Abstract: To address the prevalent social and psychological health issues stemming from the inadequate expression of architectural emotion,an empirical study was conducted on the visual perception characteristics of the rural landscape in Linjiahe Village,Southern Hebei Province,leveraging eye-tracking technology. By establishing an evaluation system encompassing four key elements: roads, boundaries, nodes,and landmarks,and adopting a methodology that integrates subjective and objective analyses, the study identified notable issues in the current rural landscape,including the absence of a visual focus and attention dispersion. Importantly,optimized design was found to substantially enhance participants’ visual attention in critical scenes.Furthermore,theresearch unveiled a clear interval efect between spatial feature parameters,such as green vision ratio and enclosure degree,and visual perception outcomes. Specifically,optimal visual perception was achieved with a green vision ratio ranging from 20% to 40% ,an enclosure degree of 50% to 60% ,an openness of 12% to 26% ,and a visual discriminability of 10% to 31% . This discovery offers a quantitative evaluation approach and optimization strategies grounded in visual perception for rural landscape design.
Key words:rural landscape design;quantitative emotional technology ;eye tracking;visual perception optimization
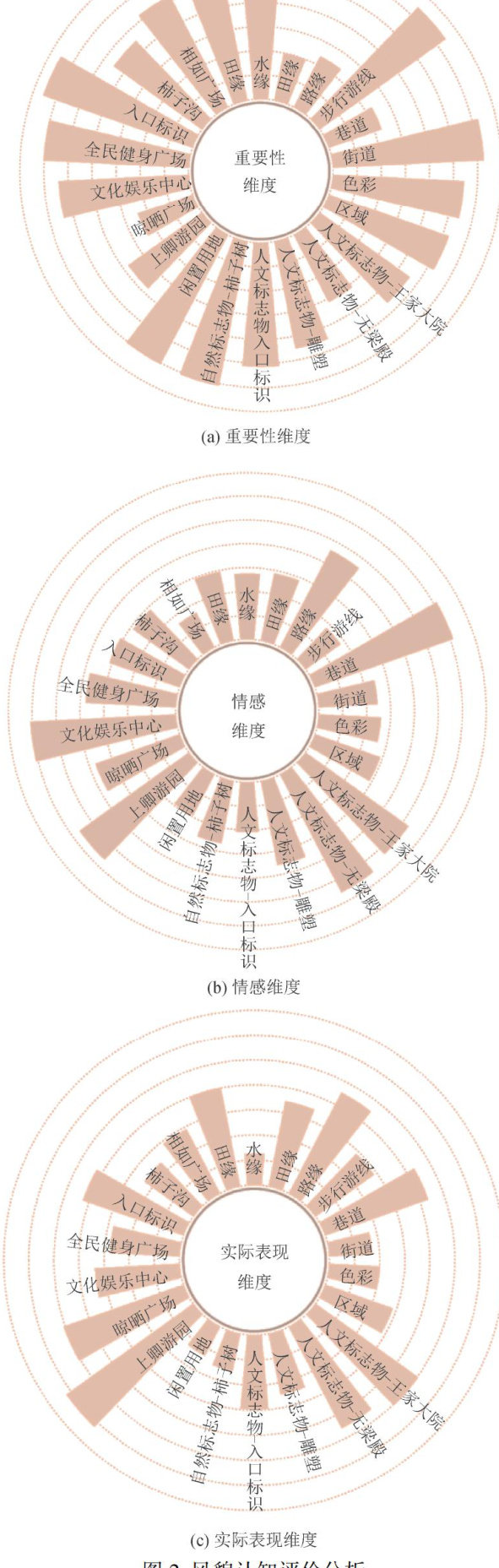
随着对健康定义的重新认知以及当下建筑情感失语加剧引发的社会心理健康危机,健康的内涵已从传统的机体健康扩展到生理、心理健康等多个方面。(剩余8727字)