不同形态氮添加对晋北农牧交错带草地生物量的影响
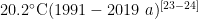
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S812.2 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1007-0435(2025)07-2198-08
doi:10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2025.07.015
引用格式:,等.不同形态氮添加对晋北农牧交错带草地生物量的影响[J].草地学报,2025,33(7):2198一2205ZHONG Hua,HAO Jie,LIANG Wen-jun,et al.Effcts of Various Nitrogen Forms Addition on Grassland Biomassin the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone in Northern Shanxi[J].Acta Agrestia Sinica,2O25,33(7):2198-2205
Effects of Various Nitrogen Forms Addition on Grassland Biomass in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone in Northern Shanxi
ZHONG Hua 1,3,4 ,HAO Jie 2,3,4 , LIANG Wen-jun 1,3,4. , Gao Yang-yang .1,3,4 ,LI Lang 1,3,4 , WANG Ya-nan 1,3,4 WANG Chang-hui 1,3,4 , DONG Kuan-hu1.3.4* (1.Collgedsit;i
AgriculturalUesitigirceinaKboatosdlocaroteo Germplasm InnovationTaiguhaniProvince3O8o,China;4.YouuLoessPlateauGassandEcosystemResearchStatonYouy, Shanxi Province O37200,China)
Abstract:At present,the effects of various nitrogen forms on grassland productivity in the Agro-pastoral eco tone of northern Shanxi remain poorly elucidated.To investigate the efects on grassand biomass and its allocation between aboveground and belowground components,the study was conducted with six treatments:control,ammonium nitrate,ammonium sulfate,ammonium bicarbonate,urea,and slow-release urea.The results showed that various forms of nitrogen adition increased aboveground,belowground,and total biomass by increasing plant community diversity,height,and cover. Notably,the addition of NH4NO3 significantly elevated soil inorganic nitrogen content,resulting in the greatest increase in aboveground biomassIn contrast, the urea treatment resulted in a moderate rise in soil inorganic nitrogen,which promoted root growth and thus increased the alocation ratioof belowground biomass.This study revealed the varied efects of various nitrogen forms on plant biomass allocation and emphasized the positive effect of a urea input of 10g⋅m-2⋅a-1 on maintain ing the productivity of grasslands in the Agro-pastoral ecotone of northern Shanxi.
Key words: Biomass;Nitrogen compounds ; Agro-pastoral ecotone; Plant communities ;Urea
自20世纪中期以来,随着化石燃料燃烧和农业化肥的大量使用,使得陆地生态系统活性氮输入急剧增加[1]。(剩余14339字)