自组装多肽及其抗菌作用研究进展

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:R75 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673-3851(2025)07-0580-08
引用格式:,等.自组装多肽及其抗菌作用研究进展[J.浙江理工大学学报(自然科学),2025,53(4):580-587.
Abstract: Bacterial infections constitute a common public health challenge, as the escalating antimicrobial resistance significantly compromises the therapeutic eficacy of conventional antibiotics. Distinct from conventional antibiotics and chemical agents,self-assembling peptides can achieve broadspectrum antibacterial efects through bacterial membrane disruption and synergistic enhancement of other antimicrobial components,demonstrating advantages including rapid bactericidal action and low resistance induction potential. Furthermore,these peptides demonstrate exceptional molecular design flexibility, targeting specificity,and environmental responsiveness, positioning them as promising candidates for Overcoming current antimicrobial resistance challenges. Recent research advancements have focused on molecular structure optimization, development of stimuli-responsive materials,and engineering of in vivo delivery systems, achieving important progress in wound dressng applications and targeted drug delivery. This review systematically examines the antimicrobial mechanisms,molecular design principles,and clinical translation progress of self-assembling peptides,while discussing future research directions and challenges.The analysis provides both theoretical frameworks and practical reference for developing nextgeneration antimicrobial self-assembling peptide-based therapeutics.
Key words:biomaterials;self-assembling peptides;bacterial infections;antimicrobial mechanisms drug delivery; molecular design
0 引言
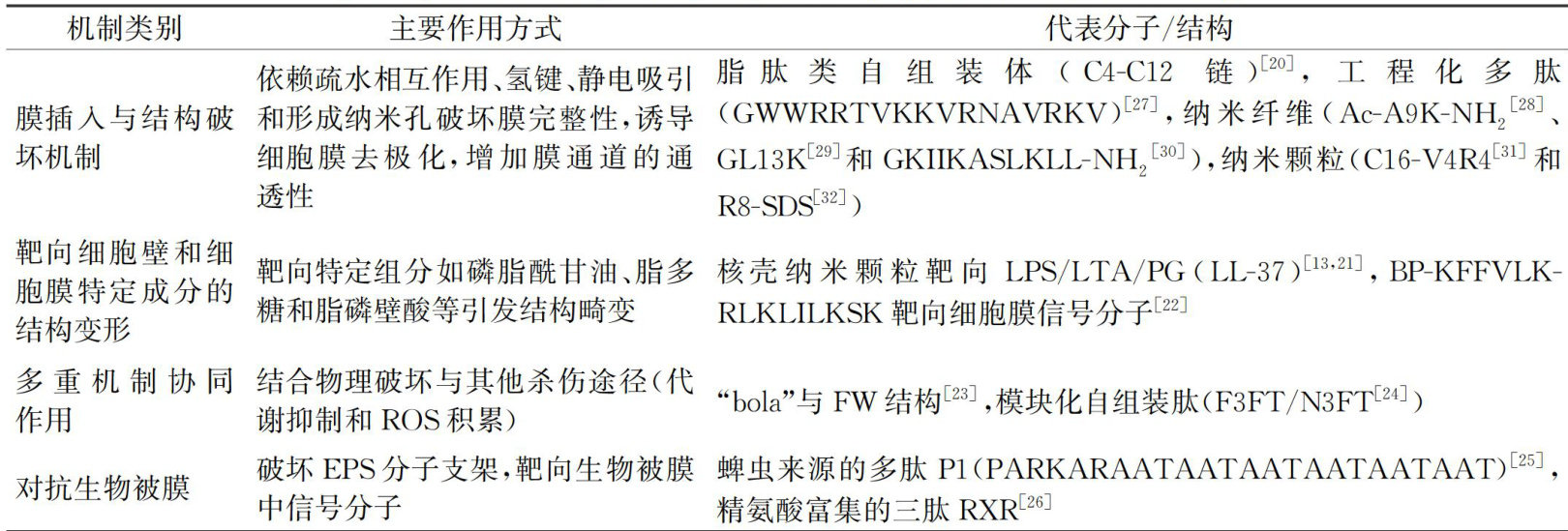
细菌感染对公共卫生安全构成重大威胁,其引发的疾病可累及全身各器官系统,严重危害人类健康[]。(剩余19282字)