抗肠球菌生物膜药物的研究进展

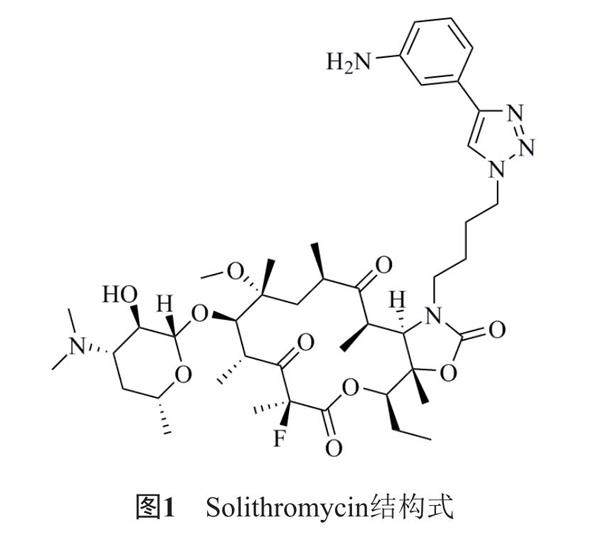
打开文本图片集
摘要:肠球菌已成为难以治疗的院内和社区获得性感染的主要原因之一。形成生物膜的肠球菌可以显著降低细菌对抗生素的敏感性,逃避宿主的免疫系统攻击,导致感染时间延长。因此开发新药物来应对抗肠球菌生物膜这一挑战是非常有必要的,本文就抗肠球菌生物膜的几种药物进行综述,以期为临床提供指导。
关键词:肠球菌;生物膜;抗感染;抗生物膜,新型药物
中图分类号:R978.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1001-8751(2023)04-0224-06
Research Progress of Anti-Enterococcal Biofilm Drugs
Cao Yang1,Zhao Jian-ping2
(1 Inner Mongolia Clinical Medical College, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010050;
2 Department of Laboratory Medicine, Inner Mongolia People’s Hospital, Hohhot 010000)
Abstract:Enterococcus has become the main cause of hospital-acquired and community-acquired infections that are difficult to treat. The biofilm-forming Enterococcus can significantly reduce the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics and evade the host's immune system attack, resulting in prolonged infection time. Therefore, it is necessary to develop new drugs to deal with the challenge of Enterococcus biofilm. This article reviews several drugs against Enterococcus biofilm in order to provide guidance for clinical practice.
Key words:Enterococcus; biofilm; anti-infection; anti-biofilm; new chemotherapeutics
肠球菌属革兰阳性菌,广泛存在于环境以及人、动物消化道内,能够在高盐(6.5% NaCl)、碱性(pH 9.6)、40%胆汁培养基、10~45 ℃等环境下生长,对多种环境具有高度耐受性,这有助于其在不同的宿主内定植并在环境中持久存在[1]。(剩余15858字)