基于混合增强大语言模型的建筑隐含碳排放预测建模方法

打开文本图片集
Abstract:Under the "dual carbon"goals,the building industry,asamajor carbon-emitting sector,is characterized by concentrated and highintensityembodied carbonemissions.Accurate prediction of building embodied carbon emissions is critical for supporting decision-making in low-carbon building design.Existing methods require extensive types of building information inputs,involve heavy computational workloads,and are time-consuming.Constrained by missing component parametersduringearlydesign stages,their prediction accuracy needs improvement,while theyalso face challenges such as high data costs,difficulties in integrating multi-source heterogeneous data,and insufficient identificationof dynamic key factors.This paper proposesa modeling method for predicting building embodied carbon emissions based ona hybrid-enhanced large language model (LLM), integrating model fine-tuning,retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and prompt engineering techniques to enhance the reasoning and prediction capabilities of LLMs in this domain.By leveraging building mass information, the method intelligently complements missing building component parameters in early design phases,enabling endto-end embodied carbon prediction.This approach addresses the limitationof existingmethods that rely heavilyondetailed buildingdata andare thus less suitable for earlydesign stages,providing predictive methodological support for low-carbon building design decisions.
Keywords:Embodied carbon prediction;Residential buildings; Large language model; Green Building; Computational design
1.绪论
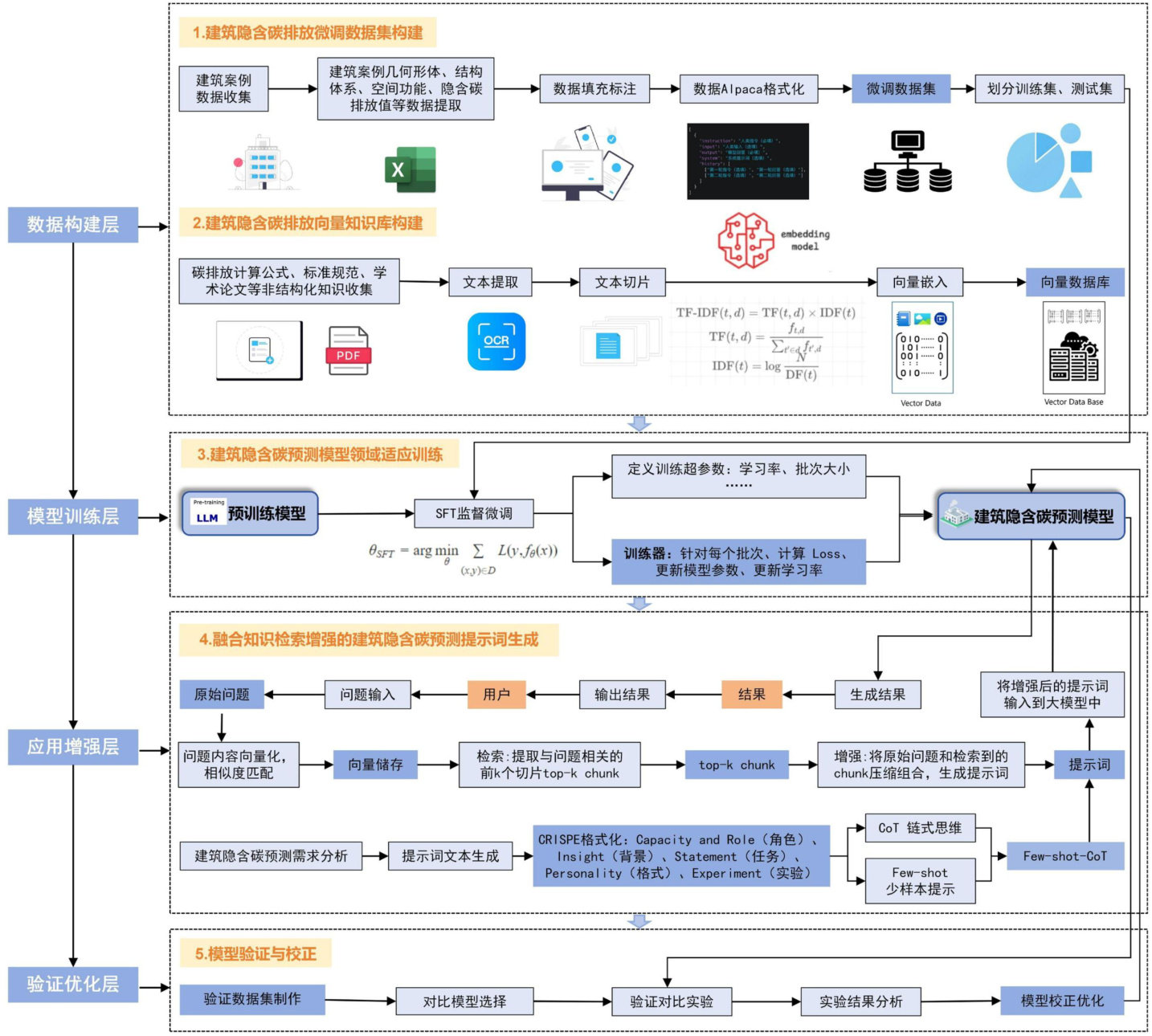
2024年,联合国环境规划署(UNEP)在《全球建筑与施工状况报告》中指出全球每年约 37% 的碳排放量来自建筑,其中仅隐含碳就占据了全球每年总碳排放量的约 11%[1] 。(剩余11977字)