磷灰石结构碳酸盐团簇同位素测温法研究进展

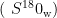
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P597 DOI:10.16152/j. cnki. xdxbzr. 2025-03-014
Research progress in clumped isotope thermometry of apatite structural carbonate
CHEN Yanlong,XI Haibin,WANG Peiyao (Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Early Life and Environments/State Key Laboratory of
Continental Evolution and Early Life/Department of Geology,Northwest University,Xi'an 710069,China)
AbstractReconstructing paleo-temperatures is of great significance for understanding the Earth’s climate changes and the evolution of life. Traditional thermometry based on δ180 has uncertainties due to its reliance on the oxygen isotope composition of seawater (F180w) . Carbonate clumped isotope ( Δ47 )thermometry, which was developed over the past 2O years,has become a research hotspot as it does not require prior knowledge of F18Ow . However,carbonates,which are the most commonly used material for Δ47 thermometry,are highly susceptible to diagenetic alteration,sometimes leading to the loss of original temperature information. Therefore,apatite,which contains structurally bound carbonate and exhibits strong resistance to diagenetic modification,has been an ideal material for studying deep-time paleoclimates.This paper reviews the research on apatite clumped isotopes, discussng the issues in the calibration relationships between apatite Δ47 and temperature,as well as potential kinetic efects.Additionally,factors such as organic matter content,kinetic effects,and diagenetic processs (recrystallization and solid-state reordering effcts)may all introduce biases in thermometric results.In the future,it will be necessary to refine thecalibration relationships,integrate multi-isotope and trace element analyses to enhance data reliability.With further research,apatite clumped isotope technology is expected to bring breakthroughs to studies in deep-time paleoclimatology and related fields.
Keywordsbiogenic apatite;carbonate; clumped isotope;palaeotemperature; kinetic effects
生物多样性往往与其生活的环境温度之间具有显著的相关性,因此古温度重建对于理解地球过去的生命演化甚至气候变化至关重要。(剩余25882字)