T淋巴细胞在原发性硬化性胆管炎中的作用

打开文本图片集
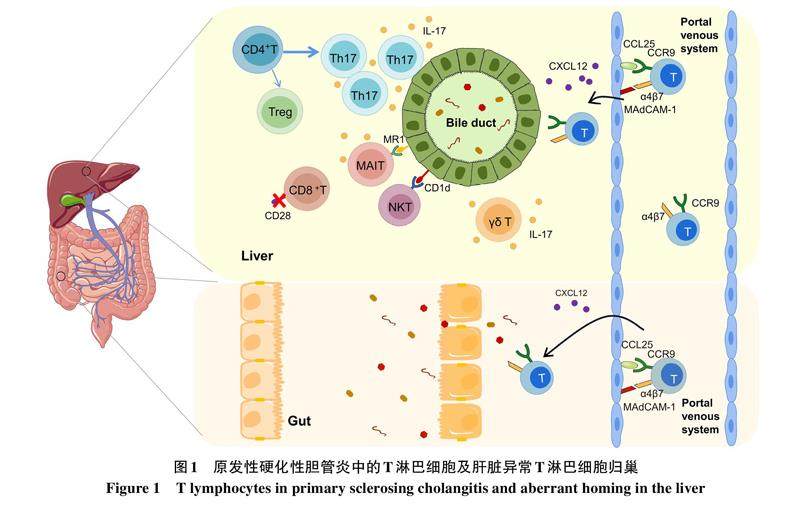
摘要: 原发性硬化性胆管炎(PSC)是一种免疫介导的慢性胆汁淤积性肝病,可进展为肝硬化和肝衰竭等终末期肝病,目前尚无有效的治疗方法。研究发现,T淋巴细胞与PSC的发生发展密切相关。现对T淋巴细胞在PSC中的作用进行综述,以期为PSC发病机制的研究及临床诊疗提供新的思路。
关键词: T淋巴细胞; 原发性硬化性胆管炎; 发病机制
基金项目: 甘肃省自然科学基金(21JR1RA070); 兰州大学第一医院院内基金(ldyyyn2020-02, ldyyyn2020-14); 甘肃省感染肝病临床医学研究中心(21JR7RA392); 甘肃省高等学校创新能力提升项目(2020B-016)
Role of T lymphocytes in primary sclerosing cholangitis
LI Ziyi1, ZHANG Wanjie1, WANG Fuchun1, MAO Xiaorong1,2a, LI Junfeng1,2a,2b. (1. The First Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China; 2. a. Department of Infectious Diseases, b. Department of Infectious Diseases & Institute of Infectious Diseases, The First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China)
Corresponding authors: MAO Xiaorong, mxr2013@126.com (ORCID: 0000-0003-1952-1554); LI Junfeng, junfenglee@126.com (ORCID: 0000-0002-5638-706X)
Abstract: Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is an immune-mediated chronic cholestatic liver disease and can progress to end-stage liver diseases such as liver cirrhosis and liver failure, and there are still no effective treatment methods at present. Studies have found that T lymphocytes are closely associated with the development and progression of PSC. This article reviews the role of T lymphocytes in PSC, so as to provide new ideas for research on the pathogenesis of PSC and the clinical diagnosis and treatment of PSC.
Key words: T lymphocytes; Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis; Pathogenesis
Research funding: Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (21JR1RA070); Hospital Fund of the First Hospital of Lanzhou University (ldyyyn2020-02, ldyyyn2020-14); Gansu Clinical Medieal Research Center of Infection & Liver Diseases (21JR7RA392); Gansu Provincial Higher Education Project on Innovation Ability Improvement (2020B-016)
原发性硬化性胆管炎(PSC)是一种免疫介导的慢性胆汁淤积性肝病,其特征是肝内外胆管炎症及纤维化导致多灶性胆管狭窄、慢性胆汁淤积,可进展为肝硬化及终末期肝病,且患胆管癌的风险增加[1]。(剩余12867字)