特基拉芽孢杆菌喷叶和灌根处理对油茶防御反应的诱导机制

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S432.2 文献标志码:A
文章编号:1001-411X(2025)06-0895-12
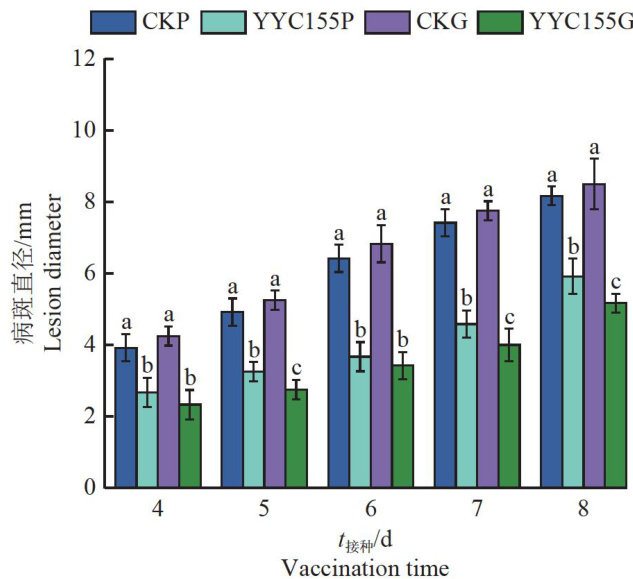
Abstract: 【Objective】 This study aimed to investigate the induction mechanism of defense responses in Camellia oleifera induced by different application methods (leaf spraying and root irigation) of Bacillus tequilensis. 【Method】B. tequilensis YYC155, which exhibits strong inhibitory effcts against Coletotrichum fructicola (the causal agent of anthracnose on C. oleifera), was employed to induce defense responsesin C oleifera seedlings through leaf spraying and root irrigation treatments. Subsequently, the activities of defenserelated enzymes and the contents of substance compounds were determined,and transcriptomic analysis was conducted to elucidate the underlying regulatory mechanisms. 【Result】 Compared with the control group, both treatments significantly enhanced the activities of defense-related enzymes in C. oleifera, including phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), cinnamate-4-hydroxylase (C4H), 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase (4CL), and chalcone isomerase (CHS). Additionally, these treatments promoted the accumulation of total phenols and flavonoids. Transcriptomic analysis revealed that there were 652 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) identified between leaf spraying samples (YYC155P) and root irrigation samples (YYC155G), which were enriched in66 KEGG pathways. Amongthese pathways, 72.41% ofthe DEGsin the four antioxidant system related pathways were upregulated, while 47.37% of the DEGs in the eight secondary metabolism-related pathways were upregulated. 【Conclusion】 Leaf spraying treatment primarily activates defense responses in C oleifera through secondary metabolic pathways,whereas root irigation treatment relies more on the enhancement of the antioxidant system.
Keywords:Bacillus tequilensis; Induction;Defense response; Camellia oleifera
油茶Camelliaoleifera隶属于山茶科Theaceae山茶属Camellia,油茶成熟种子中提取的茶油富含大量不饱和脂肪酸,是一种优质的植物油,极具营养价值[1。(剩余15125字)