酸碱腐蚀作用下含孔砂岩试件动力学性能试验研究

打开文本图片集
关键词:砂岩;动力学特性;酸碱腐蚀;冲击速度;冲击压缩;SHPB试验装置;损伤机理;深部工程中图分类号: TD322 文献标志码:A doi:10.12415/j.issn.1671-7872.24152
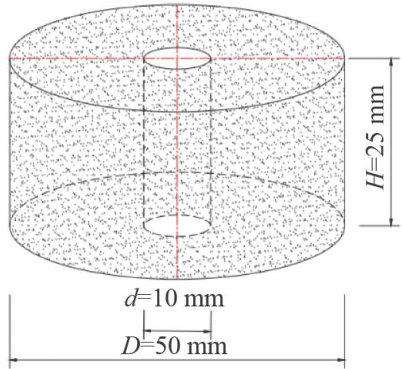
Abstract: The standard annular sandstone specimens with a central hole (outer diameter 50mm ,inner diameter 10mm )were investigated.A 28d corrosion tests in acidic (pH=5 )and alkaline (pH=9) ) solutions were conducted to analyze the evolution of physical parameters,mineral composition,and microstructure under diferent corrosive environments.The coupling relationship between acid-alkali corrosion and the physicochemical damage mechanism of sandstone,as well as dynamic mechanical behavior, was explored using split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) dynamic impact compresson tests.The results show that the acidic environment primarily induces the disolution of cations such as Na+ , Al3+ ,and Fe3+ ,accompanied by the formation of white silicic acid (H2SiO3-. )precipitates, while the alkaline environment mainly generates soluble products such as Al(OH)4- and H2SiO42- .The dynamic compressive strength and dynamic elastic modulus of the specimens increase exponentially with impact velocity, whereas the dynamic peak strain and average strain rate follow a quadratic growth pattrn.The dynamic compressive strength and elastic modulus under alkaline corrosion are superior to those under acidic corrosion,but alldynamic mechanical performance parametersin both acidic and alkaline environments exhibit significant degradation compared to those ina neutral environment.Furthermore,asthe impact velocity increases,the fragmentation degree of the specimens intensifies,and the average particle size of the fragments decreases.These findings reveal the damage accumulation mechanism of holed sandstone under chemo-mechanical coupling efects,providing a theoretical basis for evaluating the long-term stability of underground rock masses.
Keywords:sandstone; dynamical characteristic; acid and alkali corosion; impact velocity; shock compression; SHPB test apparatus; damage mechanisms; deep engineering
岩体作为典型地质介质,具有显著的不连续性、非均质性和各向异性特征。(剩余13963字)