锌元素在高炉中的分布及其对焦炭性能的影响

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TF526.1 文献标志码:A doi:10.12415/j.issn.1671-7872.24140
Abstract:A segmented heating blast furmace simulation experiment was conducted to investigate the migration behavior of zinc during iron ore reduction and softening-melting processs.The reduction-volatilization characteristics of zinc under diferent charging methods (top/bosh)and their impacts on blast furnace smelting were analyzed.The results indicate that zinc is predominantly enriched in the topdust and coke regardless of whether top charging orbosh injection is employed, with extremelylow zinc content detected in thehot metal. When ZnO blocks are introduced through top charging,comparable zinc contents are observed between the top dust and coke. In contrast, when ZnO blocks are injected through the bosh, the zinc content in the top dust is significantly higher than that in the coke, which is atributed to the rapid penetration of zinc vapor through the burden layer after being subjected to high-temperature reduction at the bosh region,resulting inshorter residence time in the coke.The catalytic efectof zinc oncoke disolution loss isdemonstrated,leading to increased coke reactivityand decreased post-reaction strength,with the mechanism explained by the promotionof ketone group decomposition and CO generationreactions.This study reveals the distribution patern of zinc within the blast furnace and its influence mechanism on coke performance.
Keywords:zinc loading; coke degradation; blast furnace operation; post-reaction strength;catalytic mechanism; low carbon iron-smelting; zinc volatilization; cyclic enrichment
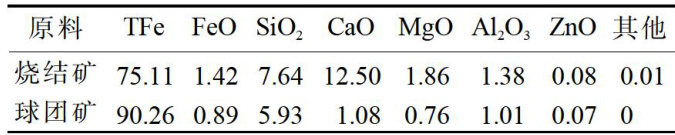
确保高炉长寿是提升高炉生产效率和降低成本的关键,对推动钢铁工业绿色高质量发展具有重要意义。(剩余12248字)