二甲醚掺混对氨/空气预混燃烧特性的影响

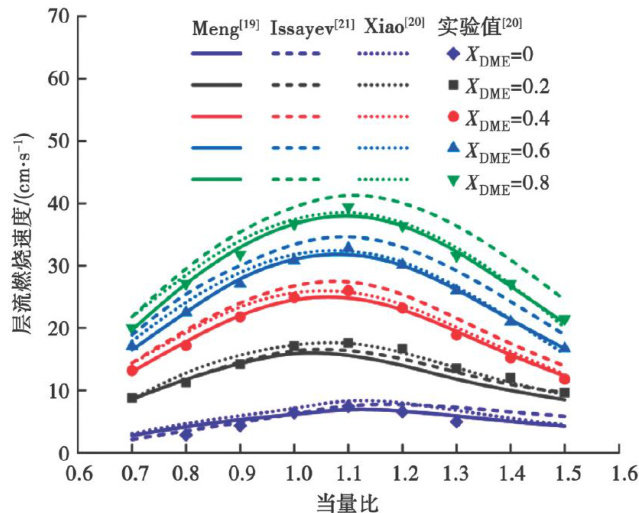
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TK411.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1000-582X(2025)07-085-09
Effect of dimethyl ether addition on NH3. /airpremixed flames
LI Tianxi,CHEN Zhaoyang,KANG Qi,ZHANG Da (School ofEnergy and Electrical Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 71O064,P.R.China)
Abstract: To improve the ignition and combustion performance of NH3 in engines,blendingitwith the highreactivity-fuel dimethyl ether (DME) is an effective strategy. This study conducts simulations of NH3/DME/air (20 premixed laminar flames to investigate the efects of DME addition on key combustion characteristics,including laminar flame speed,reaction pathways,and NO formation.The results show that both the adiabatic flame temperature and the laminar flame speed increase significantly with higher DME blending ratios.A strong correlation is observed between laminar flame speed and the concentration of reactive free radicals,suggesting that the increased radical concentration due to DMEisthe main contributor to the enhanced flame speed. Furthermore,the normalized NO concentration in the flame rises significantly with increasing DME content, reaching approximately 50% when the DME blending ratio reaches 80% . Reaction pathway analysis indicates that DME addition inhibits the conversion of nitrogen species to N2 ,thereby leading to increased NO emissions. Sensitivity analysis shows that DME significantly alters the dominant elementary reactions.As the DME ratio increases,thesensitivity of nitrogen-group reactions considerably declines,while hydrogen-and carbon-group reactions increasingly govern the combustion process of the blended fuel.
Keywords: ammonia; reaction kinetics; dimethyl ether blending; laminar flame speed; reaction pathways
随着化石能源的开采和利用,温室气体排放引起的全球气候问题成了世界性的重要议题。(剩余12917字)