继发性与特发性良性阵发性位置性眩晕临床特征及预后比较分析

打开文本图片集
Comparative analysis of clinical features and prognosis of secondary and idiopathic benign paroxysmal positconalvertigoLiLing,LiLan,QinChenchen."DepartmentofOtorhinolaryngology,Deyang People'sHospital, Sichuan 618100, China
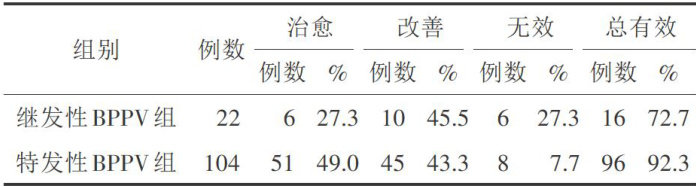
【Abstract】 ObjectiveTo compare the clinical characteristics and prognosis of patients with secondary andidiopathicbenignparoxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).MethodsTheclinical data of126patients with BPPV admited toour hospital from January2021 to September 2023 was retrospectivelyanalyzed,and they were classified into the secondary BPPV groupand the idiopathic BPPV groupaccording to the cause of their onset. The clinical characteristics,treatmentefect,qualityof lifeand prognosis of thetwo groups werecompared.Results Thepercentage of hypertension,thepercentage of moderate vertigo,and thepercentageof posterior hemicircular canal involvement were lower in the secondary BPPV group than in the idiopathic BPPV group,and the duration of persistent vertigo,severe vertigo,the percentage of anterior hemicircularcanal involvement,and thepercentage ofhorizontal hemicircular canal involvement were higher than those in the idiopathic BPPV group(all P <0.05). The total effctive rate of the idiopathic BPPV group was higher than that of thesecondary BPPV group in both the first reset treatment and after 3 months of treatment ( P <0.05).After 3 months of treatment,the Dizziness Handicap Inventory(DHI) scores of both groups were reduced,and the idiopathic BPPV group was lower than that of thesecondary BPPV group( P <0.05).The recurrence rate of the idiopathic BPPV group was lower than that of the secondary BPPV group ( P<0.05) .Conclusion Vertigo symptoms were more serious in patients with secondary BPPV,and the patients mostlyinvolved the horizontal or anterior semicircularcanal;the treatment success rate of idiopathic BPPV was higher and the recurrence rate was lower.
【Key Words】 Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo;Secondary; Idiopathic; Prognosis
良性阵发性位置性眩晕(BPPV是一种常见的内耳疾病,其特点是在头部位置改变时出现突发性的眩晕感,其主要病因为内耳半规管中的耳石脱落并进入半规管的后庭或水平道中,这些耳石的移动会导致半规管内液体的异常刺激,从而产生眩晕感[1,2]。(剩余6033字)