镧系金属螯合物作为CEST磁共振造影剂的研究进展

打开文本图片集
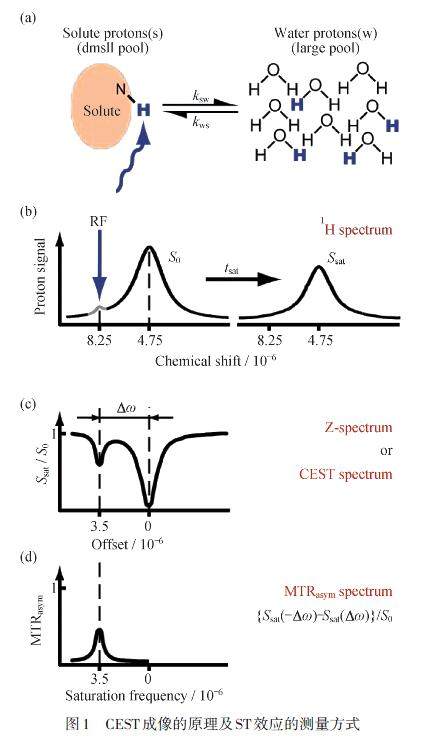
摘 要: 化学交换饱和转移(CEST)成像是一种基于化学位移现象的新型磁共振成像(MRI),通过检测水质子信号变化来间接测定可交换质子的信息,而镧系金属螯合物的顺磁化学位移大,质子共振位移更远离水的信号,可实现更多的选择性饱和,提高MRI的对比性,因此非常适合用作CEST造影剂. 镧系金属螯合物CEST造影剂具有进一步扩展磁共振功能和分子成像的巨大潜力,文章主要介绍了此类物质的类型及应用.
关键词: 镧系金属螯合物; 化学交换饱和转移(CEST); 磁共振成像(MRI); 造影剂
中图分类号: O 614.33; R 318.6 文献标志码: A 文章编号: 1000-5137(2022)04-0458-09
Research progress of lanthanide metal chelates as CEST MRI contrast agents
YANG Jingxia, JIAO Jingjing*
(College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai 200234, China)
Abstract: Chemical exchange saturation transfer(CEST) imaging is a novel magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) method based on the phenomenon of chemical shift. The information of exchangeable protons can be indirectly determined by detecting the change of water proton signal. The lanthanide metal chelates have large paramagnetic chemical shifts and their proton resonance shifts are farther away from the water signal, which is feasible to achieve more selective saturation and improve the contrast of MRI. Therefore, the lanthanide metal chelates are very suitable as CEST contrast agents and have great potentials in further expanding their magnetic resonance function and molecular imaging capabilities. This review mainly summarizes the types and applications of the lanthanide metal chelates as CEST MRI contrast agents.
Key words: lanthanide metal chelate; chemical exchange saturation transfer(CEST); magnetic resonance imaging(MRI); contrast agents
0 引 言
磁共振成像(MRI)是现如今临床放射学和生物医学研究中最有效的诊断方法之一.与计算机断层扫描(CT)相比,MRI无电离辐射,可在身体不同软组织之间提供更强的对比度.MRI是指在特定的频率激发下质子数为奇数的原子核(如氢质子)会因为能量共振而被激发,停止激发后,被激发的原子核释放能量,回到基态而产生弛豫现象,通过对氢质子信号的采集处理,可得到MRI.在现代医学中,MRI已经成为诊断和治疗人类疾病最有力的技术之一.传统MRI为了缩短弛豫时间和突出正常组织与病变组织的对比,引入了能够引起MRI信号变化的造影剂,大多数MRI造影剂都基于顺磁性螯合物,但为了降低对生理的影响,造影剂均在较低浓度下使用,这在一定程度上限制了MRI灵敏度及空间分辨率[1-2].改变组织对比度的另一种方法是更改在成像实验中检测到的水量。(剩余9069字)