大兴安岭北段库中地区早白垩世花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义

打开文本图片集
关键词:花岗岩;锆石 U-Pb 定年;地球化学;I型花岗岩;早白垩世;库中;大兴安岭北段doi:10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20250151 中图分类号:P59;P588.1 文献标志码:A
Abstract: The widespread Mesozoic granitoids in the Great Xing'an Range play a pivotal role in deciphering the tectonic-magmatic evolution of Northeast China. To constrain the emplacement age, petrogenesis,and tectonic setting of granites in the northern segment of the Great Xing'an Range,this study conducts integrated petrographic,LA - ICP- MS zircon U - Pb geochronological, zircon Hf isotopic,and whole-rock geochemical investigations on the Kuzhong granitic pluton. Zircon U - Pb geochronology yields a crystallization age of (136.5±1.7)Ma , placing the magmatic event in the Early Cretaceous.Whole-rock geochemical data reveal that the pluton represents a highly fractionated calcalkaline I-type granite,characterized by high silica (w(SiO2)=70.40%-73.54%) ,elevated alkalis (20 (w(Na2O+K2O)=8.77%-9.30%) ,enrichment in large-ion lithophile elements (e.g.,Rb,Ba),and depletion in high-field-strength elements (e.g.,Nb,Ti,P). Chondrite-normalized rare earth element patterns exhibit right-dipping trends with pronounced negative Eu anomalies. The homogeneous zircon Hf isotopic compositions (εHf(t)=5.1-8.8 , mean 6.7) suggest magma derivation predominantly from partial melting of juvenile lower crust. Synthesizing regional tectonic evidence,we propose that the Kuzhong granite formed in a post-orogenic extensional setting following the closure of the MongolOkhotsk Ocean,overprinted by lithospheric thinning and asthenospheric upweling driven by PaleoPacific plate rollback. This thermotectonic process facilitated melting of juvenile lower crustal materials, ultimately generating highly fractionated calc-alkaline I- type granites.
Key words: granite; ziron U - Pb dating; geochemistry; I - type granite; Early CretaceousKuzhong;Northern Great Xing'an Range
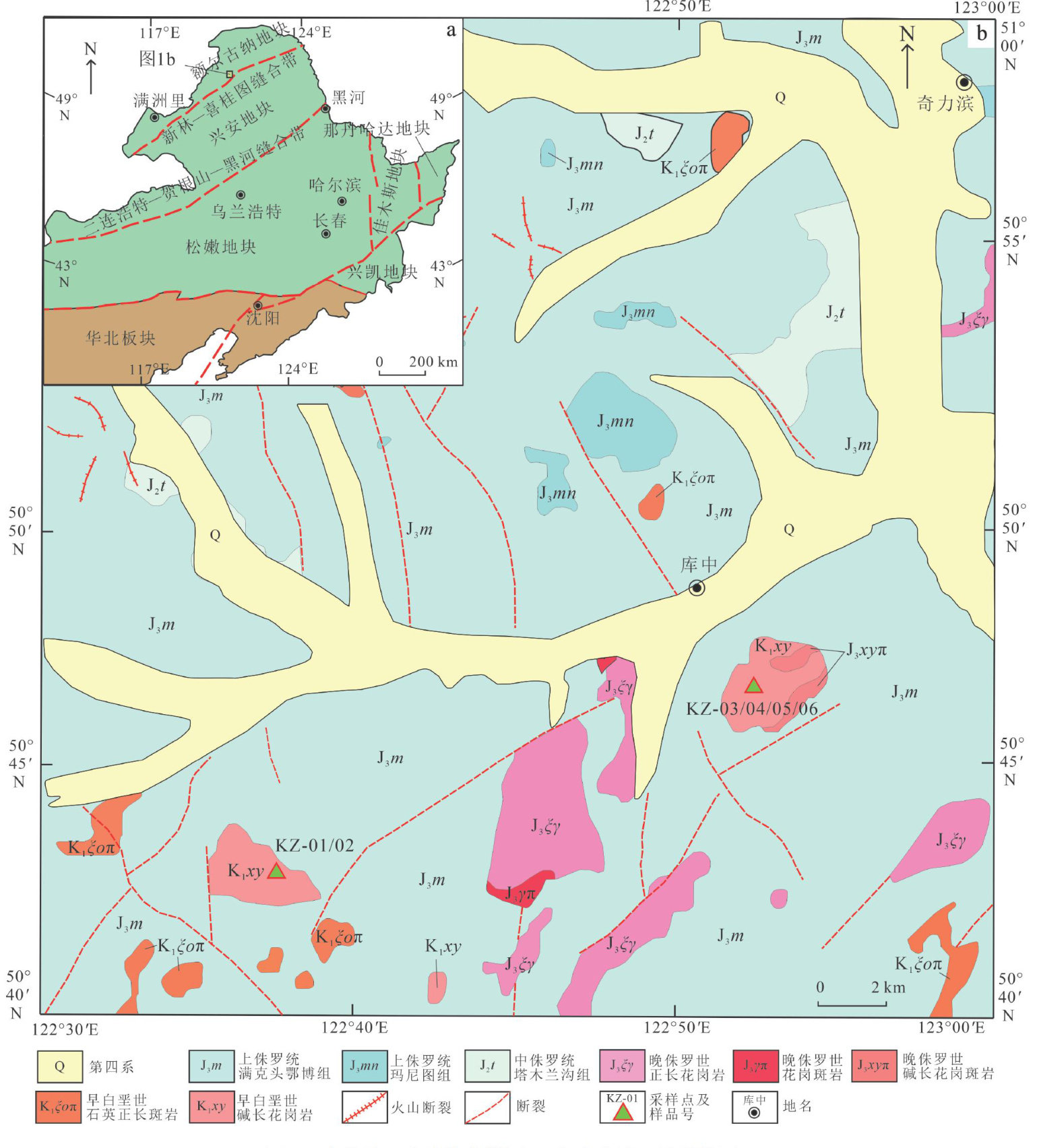
0 引言
大兴安岭地处蒙古一鄂霍茨克与环太平洋构造域交汇区,其中生代构造-岩浆活动是解析东北亚板块相互作用与深部物质循环的关键窗口[1-5]。(剩余29289字)