扬子西缘新元古代早期大洋俯冲作用
——来自川西天全闪长岩成因的制约

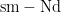
打开文本图片集
Abstract:Magmatic rocks exposed along the western margin of the Yangtze Block play a crucial role in reconstructing the Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the Yangtze Block.This study investigates diorite plutons in the Tianquan area of western Sichuan through U-Pb zircon dating, whole-rock major and trace element analysis, zircon Lu-Hf isotopic analysis, and whole-rock Sm-Nd isotope systematics. The Tianquan diorites formed 807~ (204号 804Ma ,and are characterized by moderate w(SiO2 0 55.71%~59.74% and low w(K2O)(1.10%~1.77%) ,belonging to thecalc-alkaline series.The diorites displayarc-type features,including enrichment in lightrare earth elements and large ion lithophile elements,depleted in high field strength elements,and significantly positive zircon εHf(t)(+10.0 to +12.9 Dandwhole-rock εNd(t)(+4.25 to +4.43 ).Relativelyhigh Ba/Th and low ThILa ratios suggest that the source was prmarily metasomatized by subduction-related fluids.The whole-rock geochemical signaturesand Nd-Hf isotopic compositions demonstrate that the Tianquan diorites originated from partial melting of a mantle wedge modified by subduction fluids,and the diorites were emplaced in an island arc environment.By integrating magmatic and sedimentary features along the western margin of the Yangtze Block, this study suggests that the western margin of the Yangtze Block was in a subduction tectonic setting in the early Neoproterozoic.
Key words: Tianquan diorite; geochemistry;Neoproterozoic;petrogenesis;western Yangtze Block
罗迪尼亚(Rodinia)超大陆形成是地质历史上一次重要的全球性大陆聚合事件,为宜居地球的形成奠定了重要基础,一直备受全球地质学家广泛关注(Hoffman et al.,1998,2017;Cawood et al.,2013,2018;Dong etal.,2024a)。(剩余44562字)