AtIDD6 过表达植株的构建及其表型

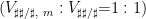
打开文本图片集
中图分类号: S635.301 文献标志码: A 文章编号: 1004–390X (2025) 02−0017−07
Abstract: [Purpose]To explore the biological function of AtIDD6 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana development. [Methods]The coding sequence of AtIDD6 was fused to the 35S promoter of cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) to construct the 35S::AtIDD6 vector, which was transformed into Arabidopsis wild type plants by inflorescence immersion of Agrobacterium. Homozygous transgenic plants of T3 generation were obtained by hygromycin screening and PCR identification. AtIDD6 expression level was detected in the transgenic plants by RT-PCR. [Results]The expression level of AtIDD6 in T3 generation transgenic A. thaliana was significantly higher than that of the wild type.
AtIDD6 overexpressed plants had smaller leaves, growth retardation, and seedling root growth significantly slowed down. The results reveal that AtIDD6 was involved in plant growth by a negatively regulated manner. [Conclusion]This study can lay a foundation for subsequent studies of the function and mechanism of AtIDD6 gene in plant growth and development.
Keywords: AtIDD6; construction of overexpressed plants; Arabidopsis thaliana
最早发现的 ID-domain 基因是玉米 INDETE-RMINATE1 (IDI) ,为典型的开花基因,ID1 突变后导致玉米植株从营养生长转向生殖生长的过程推迟[1],水稻中该基因缺失的突变体在适宜光周期下也不能进入生殖生长[2]。(剩余10620字)